Most people have suffered from a nosebleed in their lives. Nosebleeds usually occur to most people in their childhood and during hot seasons. Factors which are not that serious usually cause nosebleeds, however, in some few cases, serious factors which require urgent medical attention can also be a possible cause.
The nose has small sensitive blood vessels which can easily be damaged and start bleeding. Blood vessels which are near to the outside of the nose cause most of the nosebleeds that occur randomly. However, there are fewer nosebleeds which emanate from deep inside the nose and these are usually because of some trauma to the head.
Blood usually flows from either nostril or both during a nosebleed. There are variations in the extent of bleeding, with little bleeding occurring sometimes and severe bleeding in others. Nosebleeds usually last for a time interval of seconds to 10 minutes.
What causes nosebleeds?
Nosebleeds can be triggered by a wide range of factors for example:
- Injury to the nose,
- Variations in temperature and humidity may lead to cracking of the outer nasal membranes.
- Picking on your nose,
- Infections, for example, influenza (flu) which causes nasal congestion, sinusitis and hay fever (which is associated with allergic reactions) can also cause nosebleeds.
- Trauma or a shock to the head, for example, taking a blow to the head, banging the nose against a hard surface, and having recently had surgery are all factors that can cause nose-bleeding.
Dry nasal membranes which become cracked usually cause random nosebleeds. Climatic conditions such as hot temperatures and low humidity, which usually occur in October (in Savanna) are the major causes of dry nasal membranes, which eventually crack to trigger a nosebleed.
Blood-thinning medications, for example, warfarin can have side effects like triggering nosebleeds. Overdosing on medications like nasal decongestants can also trigger nose-bleeding. Experts therefore advise to always consult your doctor if this happens.
Who is at risk of getting nosebleeds?
Nosebleeds can happen to anyone regardless of their age. However, they usually affect children aged 2-10 years, pregnant women, people above 65 years (the elderly) and people who take blood-thinning medications like warfarin. There are other factors which may also increase the risk of nosebleeds, for example alcoholism (alcohol abuse), infections and hypertension.
How to prevent and treat nosebleeds

Applying a small amount of moisturizer inside the nose, for example, vaseline helps to prevent nosebleeds. This is because nosebleeds usually occur because of the nasal membranes cracking after drying out.
Having the heater ‘ON’, inside the house can cause the air to be dry and eventually dry out the nasal membranes. When the nasal membranes are dry, they may crack and start bleeding. It is therefore advisable to have a humidifier which keeps the air moist when the heater is ‘ON’ for prolonged periods of time.
There are other bad habits which may trigger nosebleeds which you need to stop to prevent nosebleeds, for example, picking on your nose and blowing it too hard when you have nasal/mucus congestion.
Smoking and drinking too much alcohol can expand the cells in the nasal membranes, which may eventually lead to nosebleeds. It is therefore advisable to stop smoking and drinking when you are having trouble with nosebleeds.
How to stop nosebleeds
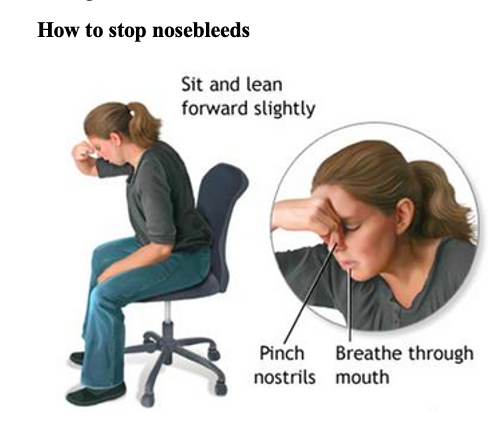
When you experience a nosebleed, you can stop it by pinching the soft part of the nose with your thumb and the finger next to it on both sides of your nose, just above your nostrils. You should then sit down and pinch your nose for 5 to 15 minutes while leaning forward and taking deep breaths with your mouth. Leaning forward helps the blood to flow out through the nose and not go down the throat.
We should consider which nose bleeding cases severe?
- We should consider cases that exceed 10minutes as serious bleeding, and if bleeding exceeds 20 minutes, it should be treated as severe.
- Cases where nose bleeding occurs after an injury on the upper part of the body, for example, the head.
How to deal with serious/ severe nose bleeding?
Seek medical attention urgently.
